Tappet Shedding
A tappet is a shedding cam which is mounted on the bottom shaft. The tappet gives rotary motion and operates the heald shaft by pressing the lever and treadle arrangement, the motion is called tappet shedding.
Scopes of Tappet Shedding:
- Cams and tappets are used to control the up / down movements of the heald shafts.
- Only plain, twill and simple sateen and satin weaves can be constructed using tappet shedding.
- By adopting tappet shedding, the loom can control only 8-12 shafts.
- Designs like elaborate twill, satin or sateen with repeat sizes more than (8x8) or (12x12) requires dobby shedding.
Positive Shedding
A tappet shedding is considered to be positive when both the up / down movements of the heald shafts are done by the mechanism of the tappet and does not require an external device.
Construction:
- The positive tappet can be distinguished into 2 parts, i) tappet and ii) heald shaft.
- Tappet shaft portion consists of tappet shaft, tappet, track and tredle bowl.
- On the other hand, a heald shaft consists of 24-36 heald wires. The heald shafts are connected by heald shaft links to fulcrum and subsequently to link rods.
- Both the tappet lever and link rods are connected among themselves with 2 separate fulcrums.
Working Principle:
The universal fact for positive tappet shedding is that both up / down movements or the whole operation does not require any sorts of external device. In this mechanism, the tappet shaft or follower (A) follows the track or the groove (C) in the tappet (B). The tappet is then got up to the tappet shaft whose movement is controlled by the main shaft. Consequently the tappet lever (E) moves right to left which get motions from the tappet shaft by fulcrum (F), moving heald shafts (K) in the process.
Negative Shedding:
A tappet shedding is considered to be negative when the up / down movements of the heald shafts require an external device (ie springs) along with the original mechanism.
Construction:
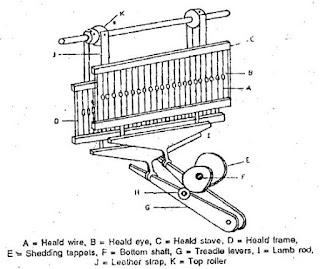
The negative tappet shedding can be divided into two separate portions, i) Bottom portion, ii) Top portion.
- Bottom portion includes two shedding tappets that are connected by bottom shaft. They are contained by two treadle levers which are connected by a fulcrum.
- The treadle levers connect top portion with bottom portion by two rods named lamb rods.
- The top portion concludes two heald stoves or heald frames which have 24-36 heald wires, each of them containing a heald eye.
- They are held up to a rotating roller shaft containing two rollers of different diameters.
Fig. 03: Negative Tappet Shedding
Working Principle:
- The bottom shaft (F) is rotated in the clockwise direction and thus gives motion to the tappet (E1).
- The tappet will press one treadle lever (G1) and anti-friction bowl, bringing down the front of the treadle in the process.
- This action brings down the lamb rod (I1) which brings down the heald shaft (C1) sending the action all the way up to the leather strap (J) or the rotating rollers. This action forms the bottom layer of the shed by lowering the mentioned heald shaft (C1).
- Lowering one heald shaft (C1) automatically raises the other heald shaft (C2) as both the shafts are connected by a leather strap (J) on a rotating roller shaft (K).
- The raised heald shaft consequently raises the lamb rod (I2) and thus the front part of the other treadle lever (G2).
- The other tappet (E2) again presses the treadle lever (G2) down consequently bringing the lamb rod (I2) and heald shaft down (C2) which pulls down its side's leather strap (J) only to raise the other heald shaft (C1). up again.
- Therefore in this mechanism two sheds are formed for one rotation of the bottom shaft (F).
Advantages of Tappet Shedding
- Its operation speed is comparatively fast.
- It is tough, elementary and inexpensive.
- Capable of lifting more weight with less damages to its structure.
- Tends to do less damage to warp.
- Needs little to no maintenance.
- It is greatly efficient in terms of energy consumption.
Disadvantages of Tappet Shedding
- If the design requires more than 10 heald shafts, the design cannot be produced using tappet shedding.
- In order to produce a different plain or twill design (limited), tappets and shaft arrangements need to be changed.
- Changing the arrangements is time consuming and relatively hard.








0 Comments